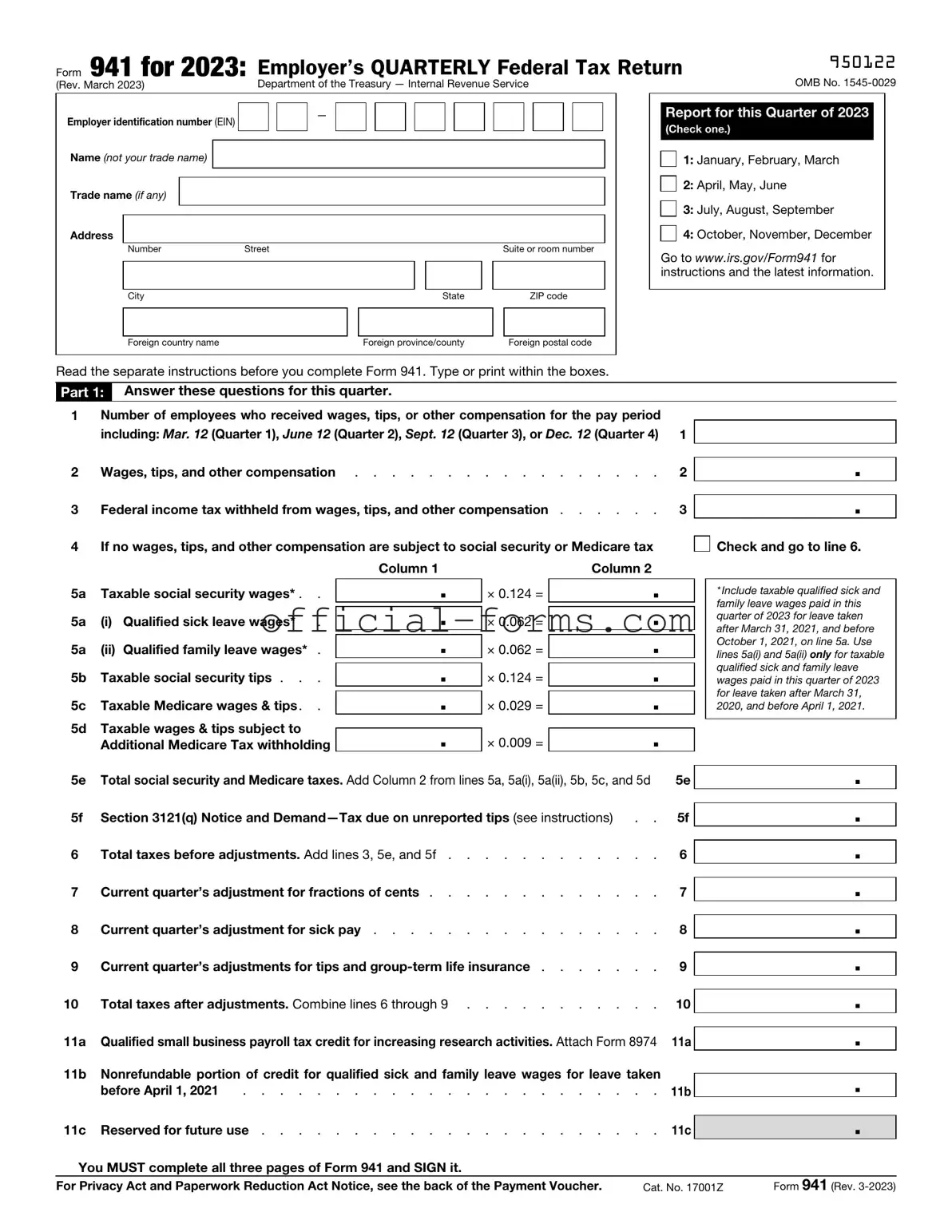
Filling out the IRS Form 941 can be a straightforward process, but many people make common mistakes that can lead to delays or penalties. One frequent error is failing to report all wages accurately. Employers must include all taxable wages, tips, and other compensation. Omitting even a small amount can result in discrepancies that raise red flags with the IRS.
Another mistake involves miscalculating the tax liability. Some individuals misinterpret the instructions or misapply the tax rates. This can lead to underreporting or overreporting the amount owed, which can trigger audits or additional penalties. Always double-check calculations to ensure accuracy.
Many people also neglect to sign and date the form. A missing signature can delay processing and cause the IRS to consider the form incomplete. This simple oversight can lead to significant complications, including late fees or additional scrutiny.
Incorrectly identifying the employer's identification number (EIN) is another common issue. The EIN must be accurate and match the IRS records. Errors in this number can result in confusion and processing delays, as the IRS may not be able to link the form to the correct employer.
Some filers forget to account for adjustments. If there were any corrections or adjustments from previous quarters, these need to be reflected on the current Form 941. Failing to include these adjustments can lead to inaccurate reporting and potential penalties.
Additionally, individuals often make mistakes regarding the quarter being reported. Each form corresponds to a specific quarter, and submitting a form for the wrong quarter can lead to unnecessary complications. Always verify the quarter before submission.
Another mistake involves misunderstanding the deadlines. The IRS has specific due dates for Form 941, and late submissions can incur penalties. It's crucial to stay informed about these deadlines to avoid unnecessary fees.
Some employers mistakenly believe they can file Form 941 annually instead of quarterly. This misconception can lead to significant compliance issues. Form 941 must be filed quarterly, and failing to do so can result in penalties.
Finally, neglecting to keep copies of submitted forms can be a costly mistake. Employers should retain copies for their records, as they may need to reference them in the future. Keeping thorough records helps ensure compliance and simplifies the process in case of an audit.